Let us inquire into the chemical nature of the materials shown in the above pictures
that we use frequently in our daily life.
At molecular level, they all have a common special feature. That is, they all are made
up of large molecules arranged in the form of long chains. Another speciality is that
most of those long chain molecules are composed of repeating small molecular
units. Thus, the molecules from which they are made are called polymers. In this
lesson, let us discuss about polymers.
Large molecules formed by the joining of a large number of small molecules
with one another are known as polymers.
The process of forming polymers is called polymerization. The small molecules
forming polymers are known as monomers and the large molecules formed by the
polymerization of monomers are referred to as polymers. Pay your attention to the
chain formed by joining some paper clips together.
The single paper clips used to form the above chain are analogous to monomers and
the chain of clips is equivalent to the polymer. The basic structural units contained
in the chain after the formation of the polymer are referred to as repeating units.
The molecular mass of monomers is relatively low. However, the relative molecular
mass of polymers formed by the polymerization of a large numbers of monomers
has a very high value.
Now, let us investigate into some common polymers.
Polythene (Polyethene)
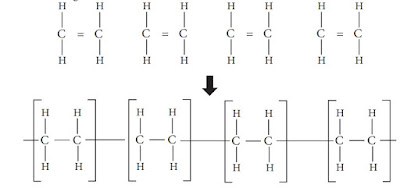
Consider the ethene molecule we learnt earlier.
Polythene is produced by the polymerization of ethene molecules. What happens
here? Of the double bond, one bond breaks and thousands of ethene molecules are
added together as shown below.
The above polymerization process may be summarized and indicated as follows.
This means that 'n' number of ethene molecules link with one another and create a
polythene molecule with 'n' number of – CH2
– CH2
– repeating units.
Hence, it may be clear to you that polythene is a macromolecule formed by the
linking of a large number of ethene molecules in a specific pattern.
The polymer, monomer and the repeating unit of polythene are given below.
Polymers - Very large molecules formed from linking together, a large
number of small molecules are named polymers.
Monomers - Small molecules contributing to form polymers are called monomers.
Repeating unit - The basic structural unit contained in a polymer are known as
repeating units.
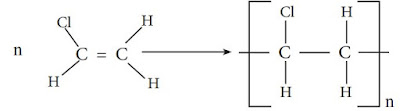
Polychloroethene (Polyvinyl chloride)
Polymerization of chloroethene gives polychloroethene. This can be summarized
as follows.
Try to identify the monomer, repeating unit and the polymer of polychloroethene.
Polytetrafluoroethene (Teflon)
Polytetrafluoroethene is formed by the polymerization of tetrafluroethene. This can
be illustrated as follows.
Identify the monomer, repeating unit and the polymer of tetrafluoroethene.
Classification of polymers based on origin
Recall the polymers you studied earlier. All of them are artificially synthesized
polymers. Have you heard about natural polymers Pay attention to the
bio - molecules you learnt in grade 10. Molecules like proteins, starch, cellulose and
DNA are polymers. They belong to the category of natural polymers. Therefore, by
origin, polymers can be classified into two types as natural and artificial. Rubber
which is frequently used for technical purposes is also a natural polymer. below Table lists some examples of natural and artificial polymers.
Rubber
Rubber is a natural polymer formed by the polymerization of a monomer called
isoprene. The structure of an isoprene molecule is given below.
The process leading to the formation of the polymer can be illustrated as follows.
Classification of polymers based on structure
All the polymers so far discussed are made of linear chains. However, all
polymers are structurally not linear polymers. By joining polymer molecules
laterally to the principle chain of the linear polymers of the type described above,
branched polymers are produced.
The polymers in which the linear chains are cross-linked are known as cross-linked
polymers. Therefore, the polymers can be classified as follows according to the
structure.
Have you heard about vulcanized rubber? Because of the elastic property of rubber,
it is difficult to be used in some applications. By vulcanization, rubber can be made
harder while decreasing its elasticity. During vulcanization natural rubber is
reacted with sulphur. Then, cross links are formed among the linear chains of rubber
through sulphur.
Vulcanized rubber is used to make tyres, tubes and battery cases.
Importance of polymers
When taking lunch away from home, natural materials such as a banana leaf or
a "Kolapatha" was used for wrapping in the past. But today, what we use for this
purpose is a type of polythene which is a synthetic polymer. Like this, at present,
artificial polymers are being used as substitutes for materials. Properties such as the
ability to synthesize with required characteristics, ease of usage, ability to produce
in various shapes, ability to make colourful with any required colour and cheapness
have made the items produced with polymers popular.
Most of the artificial polymers are not subjected to biodegradation. That is, they do
not decay through biological process. Therefore they get collected in the
environment. This is a big environmental problem. Since the combustion of
artificial polymers release poisonous gases, burning is not suitable. Chemists are
making attempts to find a solution for this problem by producing
degradable polymers. At present, production of biodegradable and photodegradable
polymers and water-soluble polymers are underway.
The clothes produced with artificial polymers such as nylon, terylene and polyester
do not absorb sweat and cause discomfort to the body. This can be minimized by
mixing natural polymers such as cotton and wool with artificial polymers.





















No comments:
Post a Comment